Vue3组件通讯
组件通讯Vue2
Props
使用案例
vue2父向子传值
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>vue2->父向子传递参数通过属性进行参数的传递</h3>
<h3>父组件</h3>
<p>userName:{{userName}}</p>
<p>age:{{age}}</p>
<hr/>
<Child :userName="userName" :age="age" hobby="1"/>
<hr/>
<!-- 上面使用子组件的语法糖,效果相同 -->
<Child v-bind="{userName,age,hobby:'1'}" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {Child},
data(){
return {
userName:"zhangsan",
age:10
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<p>props->userName->{{userName}}</p>
<p>props->age->{{age}}</p>
<p>props->hobby->{{hobby}}</p>
<p>props->sex->{{sex}}</p>
<button @click="fn">点我</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Child",
// 1- 数组,数组内的元素是字符串,字符串即是属性的名字
props:["userName","age"],
// 2- 对象:对象的属性即是接收的属性。可以对类型进行限制
props:{
userName:String,
age:Number
},
// 3- 对象
props:{
userName:{
type:String
},
age:{
type:Number
},
hobby:{
type:String,
required:true
},
sex:{
type:String,
default:"男"
}
},
methods:{
fn(){
// 可以通过this获取属性,且不允许修改
console.log(this.userName,this.age,this.hobby,this.sex);
this.userName= 1;
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>vm.$attrs
类型:{ [key: string]: string },只读。
说明: 包含了父作用域中不作为 prop 被识别 (且获取) 的 attribute 绑定 (class 和 style 除外)。当一个组件没有声明任何 prop 时,这里会包含所有父作用域的绑定,并且可以通过 v-bind="$attrs" 传入内部组件。
作用:父组件给子组件的根元素上设置的属性中,子组件没有通过Props或defineProps接收,在子组件中可以使用this.$attrs获取主组件设置的属性值。使用案例
可以通过this.$attrs获取父向子传递过来的属性
可以通过this.$listeners获取父向子传递过来的自定义事件(.native修饰符的事件获取不到)
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件App</h3>
{{ sex }}
<hr />
<Child @click="fn" a="1" b="2" c="3" :sex="sex" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Child },
data() {
return {
sex: "男"
}
},
methods: {
fn(a, b, c, d) {
console.log('fn', a, b, c, d)
this.sex = d;
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<p>a:{{ $attrs.a }}</p>
<p>b:{{ $attrs.b }}</p>
<p>c:{{ $attrs.c }}</p>
<p>sex:{{ $attrs.sex }}</p>
<button @click="test"> 点我</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 如果你在
// 可以通过this.$attrs获取父向子传递过来的属性。
// 可以通过this.$listeners获取父向子传递过来的自定义事件。
export default {
name: "Child",
methods: {
test() {
this.$listeners.click(1, 2, 3, 4);
}
},
mounted() {
console.log(this);
}
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>vm.$listeners
类型: { [key: string]: Function | Array<Function> },只读
详细: 包含了父作用域中的 (不含 .native 修饰器的) v-on 事件监听器。它可以通过 v-on="$listeners" 传入内部组件
作用:父组件给子组件的根元素上设置自定义事件中,在子组件中可以使用this.$listeners获取主组件设置的自定义事件。使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件App</h3>
{{ sex }}
<hr />
<Child @click="fn" a="1" b="2" c="3" :sex="sex" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Child },
data() {
return {
sex: "男"
}
},
methods: {
fn(a, b, c, d) {
console.log('fn', a, b, c, d)
this.sex = d;
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<p>a:{{ $attrs.a }}</p>
<p>b:{{ $attrs.b }}</p>
<p>c:{{ $attrs.c }}</p>
<p>sex:{{ $attrs.sex }}</p>
<button @click="test"> 点我</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 如果你在
// 可以通过this.$attrs获取父向子传递过来的属性。
// 可以通过this.$listeners获取父向子传递过来的自定义事件。
export default {
name: "Child",
methods: {
test() {
this.$listeners.click(1, 2, 3, 4);
}
},
mounted() {
console.log(this);
}
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>vm.$emit
在当前组件触发一个自定义事件。任何额外的参数都会传递给事件监听器的回调函数
interface ComponentPublicInstance {
$emit(event: string, ...args: any[]): void
}示例
export default {
created() {
// 仅触发事件
this.$emit('foo')
// 带有额外的参数
this.$emit('bar', 1, 2, 3)
}
}更改父组件中的数据的方式:
方式1:通过父组件向子组件传递一个函数,然后子组件调用这个函数达到子组件改变父组件数据的目的
方式2:通过自定义事件传值并修改自定义事件使用案例
vue2通过自定义事件更改数据
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>vue2->自定义事件</h3>
<h3>父组件</h3>
<!-- 添加自定义事件到子组件上 changeCount -->
<!--:count="count" 前边的count是给子组件传的属性,后边的count是父组件date中的数值-->
<!-- 添加自定义事件 changeCount 到子组件上,触发时执行后边的函数changeCount -->
<!-- 给子组件传递属性count(=前边的),值为date中的count(=后边的) -->
<Child @changeCount="changeCount" :count="count" :changeCount="changeCount"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {Child},
data(){
return {
count:100
}
},
methods:{
changeCount(count){
this.count+=count;
}
}
}
</script>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<p>count:{{count}}</p>
<!--更改父组件中的数据的方式-->
<!--方式1:子组件接收父组件传递过来的函数。当点击按钮时调用。 -->
<button @click="changeCount(3)">调用函数</button>
<!--方式2:子组件通过自定义事件 监听自定义事件-->
<button @click="$emit('changeCount',5)">调用自定义事件</button>
<button @click="fn">调用自定义事件2</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Child",
props:["count","changeCount"],
methods:{
fn(){
this.$emit("changeCount",6)
}
},
mounted(){
console.log(this)
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>Vue.prototype
通过在Vue实例的原型连上增加一个属性 Vue.prototype.$bus 实现事件总线
事件总线作用
通过使用在Vue原型上设置一个属性(.$bus),把父组件上设置的事件(this.$on("事件名"))和子组件上监听的事件(this.$emit("事件名"))串联起来(父组件和子组件的this不是同一个对象)。
通过使用 Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue()
父组件和子组件在调用 this.$bus 指向的是同一个Vue实例,这就解决了this指向不同对象的问题
事件总线的使用:父组件上设置的事件(this.$bus.$on("事件名"))和子组件上监听的事件(this.$bus.$emit("事件名")),就可以实现父子之间传值。使用案例
<div id="app">
<button @click="fn">FatherBtn</button>
<hanser ></hanser>
</div><script type="module">
// 在Vue的原型上设置一个全局属性 .$bus
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue();
Vue.component("hanser",{
data(){
return{
num:1
}
},
template:(`
<button @click="Hanser">hanserBtn</button>
`),
methods:{
Hanser(){
// VueComponent的实例;$bus属性在 VueComponent.__proto__.prototype原型上
console.log('子组件中的this',this);
// 子组件设置触发事件 Aqua,并传值
this.$bus.$emit("Aqua","mooooooooo~");
},
},
})
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
age:12
},
methods:{
fn(){
// 父组件设置触发事件 Aqua,并传值
this.$bus.$emit('Aqua',"neeeeeeeee~");
},
},
mounted(){
// Vue的实例;$bus属性在 Vue.prototype上
console.log("父组件中的this",this);
this.$bus.$on('Aqua',function(str){
console.log('Aqua',str)
})
}
})
</script>sync修饰符
在有些情况下,我们可能需要对一个 prop 进行双向绑定,即父组件和子组件之间进行数据同步。可以通过.sync修饰符和v-bind来进行实现。这样vue2会在父组件上自动创建并监听一个 update:propsName事件,子组件可以通过$listeners获取到这个事件
<template>
<div>
<h3>{{userName}}</h3>
<!--使用v-bind结合.sync修饰符-->
<Child :userName.sync="userName"/>
<!--等效于 v-bind 并监听一个事件 -->
<Child :userName="userName" @update:propsName="fun"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
export default {
name:"App",
components: {Child},
data(){
return {
userName:"zhangsan"
}
},
methods:{
fun(v){
// 接收参数,并修改绑定的数据
this.userName = v
}
}
}
</script>注意:vue3废弃掉了.sync。vue2中的.sync相当于vue3中的v-model
使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>{{userName}}</h3>
<Child :userName.sync="userName"/>
<!--上边的sync相当于下边的简写,传递一个属性userName,和一个自定义事件-->
<!-- fun 是一个伪代码,vue内部实现,作用是把新Value赋值给userName-->
<Child :userName="userName" @update:user-name="fun"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
export default {
name:"App",
components: {Child},
data(){
return {
userName:"zhangsan"
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->component->Child.vue
模版中可以直接使用$emit()触发事件,在JS中需要声明后才可以使用。
<template>
<div>
<!--触发事件并传值-->
<h3 @click="$emit('update:userName','lisi')">子组件:child-->{{userName}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Child",
props:["userName"],
mounted(){
console.log(this)
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>vm.$refs
可以借助ref属性和$refs对象获取真实的DOM,与组件结合使用可以获取组件实例:父组件获取子组件的数据状态和方法。
类型:Object,只读
详细: 一个对象,持有注册过 ref attribute 的所有 DOM 元素和组件实例。
说明:可以借助在标签上设置属性ref结合JS中使用$refs获取真实的DOM,与组件结合使用可以获取组件实例使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件App:{{userName}}</h3>
<button @click="getChildInfo">点我获取子组件信息</button>
<hr/>
<Child ref="child"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
// 获取子组件实例方案有两种:
// 1-$refs:可以借助ref与$refs获取真实的DOM,与组件结合使用可以获取组件实例。
// 2-$children:获取当前组件下使用的子组件列表(数组)
export default {
name:"App",
components: {Child},
data(){
return {
userName:"张三"
}
},
methods:{
getChildInfo(){
// this.$refs.child 即是子组件Child的实例。
console.log("getChildInfo",this.$refs.child);
// 获取子组件数据状态
console.log("getChildInfo",this.$refs.child.userName)
// 调用 子组件的方法
this.$refs.child.changeUserName("lisi");
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<p>userName:{{userName}}</p>
<p>父组件中的userName:{{$parent.userName}}</p>
<button @click="getParent">获取父组件实例</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// $parent:可以获取父组件实例
export default {
name:"Child",
data(){
return {
userName:"child"
}
},
methods:{
changeUserName(v){
this.userName = v;
},
getParent(){
console.log("child",this.$parent);
// 调用父组件中的数据状态
this.$parent.userName="MinatoAqua 2024-8-28 graduate";
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>vm.$children
获取当前组件下使用的子组件列表(数组)
类型:Array<Vue instance>,只读
详细:当前实例的直接子组件。需要注意 $children 并不保证顺序,也不是响应式的。如果你发现自己正在尝试使用 $children 来进行数据绑定,考虑使用一个数组配合 v-for 来生成子组件,并且使用 Array 作为真正的来源。
作用:$children:获取当前组件下使用的子组件列表(数组)使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件App:{{userName}}</h3>
<button @click="getChildInfo">点我获取子组件信息</button>
<hr/>
<Child ref="child"/>
<Child ref="child"/>
<Child ref="child"/>
<Child ref="child"/>
<Child ref="child"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
// 获取子组件实例方案有两种:
// 1-$refs:可以借助ref与$refs获取真实的DOM,与组件结合使用可以获取组件实例。
// 2-$children:获取当前组件下使用的子组件列表(数组)
export default {
name:"App",
components: {Child},
data(){
return {
userName:"张三"
}
},
methods:{
getChildInfo(){
// 获取当前组件下使用的第一个子组件
console.log(this.$children[0]);
// 调用子组件下的方法
this.$children[0].changeUserName("wangwu");
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<p>userName:{{userName}}</p>
<p>父组件中的userName:{{$parent.userName}}</p>
<button @click="getParent">获取父组件实例</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// $parent:可以获取父组件实例
export default {
name:"Child",
data(){
return {
userName:"child"
}
},
methods:{
changeUserName(v){
this.userName = v;
},
getParent(){
console.log("child",this.$parent);
// 调用父组件中的数据状态
this.$parent.userName="MinatoAqua 2024-8-28 graduate";
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>vm.$parent
子组件可以通过$parent获取父组件的数据状态和方法
类型:Vue instance,只读
详细:父实例,如果当前实例有的话。
使用:$parent:获取父组件的实例使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件App:{{userName}}</h3>
<hr/>
<Child ref="child"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
// 获取子组件实例方案有两种:
// 1-$refs:可以借助ref与$refs获取真实的DOM,与组件结合使用可以获取组件实例。
// 2-$children:获取当前组件下使用的子组件列表(数组)
// 3-$parent:获取父组件的实例
export default {
name:"App",
components: {Child},
data(){
return {
userName:"张三"
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<p>userName:{{userName}}</p>
<!--获取父组件中的数据状态-->
<p>父组件中的userName:{{$parent.userName}}</p>
<button @click="getParent">获取父组件实例</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// $parent:可以获取父组件实例
export default {
name:"Child",
data(){
return {
userName:"child"
}
},
methods:{
getParent(){
console.log("child",this.$parent);
// 调用父组件中的数据状态
this.$parent.userName="MinatoAqua 2024-8-28 graduate";
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>v-model(vue2)
v-model设置在子组件上,相当于向子组件传递一个value属性,并且设置了一个自定义事件。
- App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>v-model数据的双向绑定</h3>
<!-- vue2父元素数据双向绑定 -->
<input type="text" v-model="num" />{{ num }}
<!-- 上面一条v-model语句相当于传递value属性,并且监听一个input事件 -->
<input type="text" :value="num" @input="num = $event.target.value" />
<input type="text" :value="num" @input="handle($event.target.value)" />
<!-- vue2中实现父子组件数据同步 -->
<Child v-model="num" />
<!-- v-model的作用相当于传递value属性,并且设置一个自定义事件,如下 -->
<!-- 通过传递value属性,同时设置自定义事件input==向子组件传递了一个事件 input -->
<!-- 当事件触发时,会执行事件后面的处理函数handle:将接收的值作为当前状态的num值 -->
<!-- handle函数是伪代码,v-model内部是由vue自己实现的 -->
<Child :value="num" @input="handle" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "./components/Child.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Child },
data() {
return {
num: 1
}
},
methods: {
handle(v) {
this.num = v
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="less">
</style>- Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h4 style="color: red;">Child</h4>
<p>{{ value }}</p>
<button @click="fun">触发自定义事件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Child",
props: ["value"],
mounted() {
console.log(this)
},
methods: {
fun(){
this.$emit('input',20)
}
},
}
</script>组件通讯Vue3
defineProps()
为了在声明 props 和 emits 选项时获得完整的类型推导支持,我们可以使用 defineProps 和 defineEmits API
它们将自动地在 script setup 标签中可用
在vue3中相当于vue2中的Props的作用
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
foo: String
})
const emit = defineEmits(['change', 'delete'])
// setup 代码
</script>props 和 emit 也可以通过给 defineProps 和 defineEmits 传递纯类型参数的方式来声明(TS写法)
const props = defineProps<{
foo: string
bar?: number
}>()
const emit = defineEmits<{
(e: 'change', id: number): void
(e: 'update', value: string): void
}>()
// 另一种更简洁的语法
const emit = defineEmits<{
change: [id: number] // 具名元组语法
update: [value: string]
}>()特点
不需要引入,可以直接使用。已经经过setup处理过了
指定接收的属性,指定的属性可以在模板中直接使用。
在script标签中不能用(this.属性值)获取传递过来的参数。需要通过defineProps的返回值获取。
使用案例
Vue3父向子传值
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>Vue3父向子通过属性进行参数的传递</h3>
<h3>父组件App</h3>
<p>userName:{{userName}}</p>
<p>age:{{age}}</p>
<hr/>
<Child :userName="userName" :age="age" hobby="学习"/>
<hr/>
<Child v-bind="{userName,age,hobby:'学习'}"/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import {ref} from "vue";
const userName = ref("vue3");
const age = ref(12);
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child.vue 接收参数需要使用defineProps
<template>
<h3>子组件Child</h3>
<!--模版中可以直接使用defineProps传来的参数-->
<p>userName:{{ userName }}</p>
<p>age:{{ age }}</p>
<p>hobby:{{ hobby }}</p>
<p>sex:{{ sex }}</p>
<button @click="fn">点我</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
// defineProps有两个特点:
// 1- 不需要引入,可以直接使用,已经经过setup处理过了(新版本需要引入)
// 2- 指定接收的属性,指定的属性可以在模板中直接使用。
// 在script标签中不能用(this.属性值)获取传递过来的参数。需要通过defineProps的返回值获取。
// 1- 数组的形式,数组的元素是字符串,字符串是属性名
defineProps(["userName", "age"]);
// 2- 对象
defineProps({
userName:String,
age:Number
})
// 3- 对象,对象的属性值还是对象
const props = defineProps({
userName:{
type:String
},
age:{
type:Number
},
hobby:{
type:String,
required:true
},
sex:{
type:String,
default:"男"
}
});
// 3- 对象,对象的类型和默认值
const props = defineProps({
obj:{
type:Object,
default(){
return {
name:'YuukiSakuna',
age:1000
}
}
}
});
// 通过defineProps的返回值props使用传来的参数
const fn = function(){
console.log(props); // 一个Proxy类型的对象,target属性中存在着传过来的数据。
console.log(props.userName);
console.log(props.age);
console.log(props.hobby);
console.log(props.sex);
// 属性是只读的,不允许更改
props.userName="lisi"; // 警告(新版本直接报错)
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>useAttrs()
获取 父向子传来的 属性和自定义事件
可以直接使用属性在props中,通过传值过来的属性在attrs中。
Vue3中的模版中可以直接使用 $attrs() 如同Vue2中使用,但是在JS中需要使用组合式API进行获取。
useAttrs()函数的返回值是一个对象 $attrs,这个对象中包含父组件在子组件上传递的属性attrs以及自定义事件"On+[父组件自定义事件名]"。
props的优先级高于attrs(如果在props当中声明了一个数据状态,那么attrs中不会存在与其同名的属性。)
相较于vue2中的$attrs而言通过useAttrs获取到的不仅仅是属性也包含自定义的事件。
useAttrs运行的结果是vue2中的$attrs与$listeners的一个结合体。
如果需要,你可以在 <script setup> 中使用 useAttrs() API 来访问一个组件的所有透传 attribute:
<script setup>
import { useAttrs } from 'vue'
const attrs = useAttrs()
</script>如果没有使用 <script setup>,attrs 会作为 setup() 上下文对象的一个属性暴露:
export default {
setup(props, ctx) {
// 透传 attribute 被暴露为 ctx.attrs
console.log(ctx.attrs)
}
}需要注意的是,虽然这里的 attrs 对象总是反映为最新的透传 attribute,但它并不是响应式的 (考虑到性能因素)。你不能通过侦听器去监听它的变化。如果你需要响应性,可以使用 prop。或者你也可以使用 onUpdated() 使得在每次更新时结合最新的 attrs 执行副作用。
使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>我是父组件App{{count}}</h3>
<hr/>
<Child @click="fn" a="1" b="2" c="3" :count="count"/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import {ref} from "vue";
const count = ref(100);
const fn = function(a,b,c,d){
console.log("fn",a,b,c,d);
count.value = a+b+c+d+count.value;
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<h3>我是子组件Child</h3>
<p>{{$attrs}}</p>
<p>{{$attrs.onClick}}</p>
<button @click="$attrs.onClick(1,2,3,4)">点我</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
// 模板中可以直接使用$attrs如同Vue2中一样
// JS中使用组合API->useAttrs获取attrs对象
// props的优先级高于attrs,解释:(如果在props当中声明了一个数据状态,那么attrs中不会存在与其同名的。)
// 相较于vue2中的$attrs而言通过useAttrs获取到的不仅仅是属性也包含自定义的事件。
// 即:useAttrs运行的结果是vue2中的$attrs与$listeners的一个结合体。
import {useAttrs} from "vue";
const $attrs = useAttrs(); //Proxy类型的对象
// const props = defineProps(["count"]);
console.log($attrs); // 包含属性attrs和自定义事件。
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>修改配置文件
.eslintrc.js
module.exports = {
globals: {
defineProps: 'readonly',
defineEmits: 'readonly',
defineExpose: 'readonly',
},
}
// 重启项目或在package.js中添加 "vue/setup-compiler-macros": true
"eslintConfig": {
"root": true,
"env": {
"node": true,
"vue/setup-compiler-macros": true
},
"extends": [
"plugin:vue/vue3-essential",
"eslint:recommended"
],
"parserOptions": {
"parser": "babel-eslint"
},
"rules": {
"no-unused-vars": "off",
"no-debugger": "off"
}
},defineEmits()
声明触发的事件
为了在声明 props 和 emits 选项时获得完整的类型推导支持,我们可以使用 defineProps 和 defineEmits API,它们将自动地在 script setup 标签中可用
特点
// 在vue3中没有了修饰符.native
// 父组件向子组件设置的事件,对于子组件而言都会作为属性来处理。
// 在JS中需要通过调用defineEmits 实现vue2中的this.$emit
// 模版中的$emits可以直接使用,vue3已经自动编译了组件可以显式地通过 defineEmits() 宏来声明它要触发的事件:
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
foo: String
})
const emit = defineEmits(['change', 'delete'])
// setup 代码
</script>defineProps和defineEmits都是只能在<script setup>中使用的编译器宏。他们不需要导入,且会随着<script setup>的处理过程一同被编译掉。defineProps接收与props选项相同的值,defineEmits接收与emits选项相同的值。defineProps和defineEmits在选项传入后,会提供恰当的类型推导。- 传入到
defineProps和defineEmits的选项会从 setup 中提升到模块的作用域。因此,传入的选项不能引用在 setup 作用域中声明的局部变量。这样做会引起编译错误。但是,它可以引用导入的绑定,因为它们也在模块作用域内。
针对类型的 props/emit 声明
props 和 emit 也可以通过给 defineProps 和 defineEmits 传递纯类型参数的方式来声明(TS写法):
const props = defineProps<{
foo: string
bar?: number
}>()
const emit = defineEmits<{
(e: 'change', id: number): void
(e: 'update', value: string): void
}>()
// 3.3+:另一种更简洁的语法
const emit = defineEmits<{
change: [id: number] // 具名元组语法
update: [value: string]
}>()使用类型声明时的默认 props 值
针对类型的 defineProps 声明的不足之处在于,它没有可以给 props 提供默认值的方式。为了解决这个问题,我们还提供了 withDefaults 编译器宏:
export interface Props {
msg?: string
labels?: string[]
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
msg: 'hello',
labels: () => ['one', 'two']
})上面代码会被编译为等价的运行时 props 的 default 选项。此外,withDefaults 辅助函数提供了对默认值的类型检查,并确保返回的 props 的类型删除了已声明默认值的属性的可选标志。
使用案例
vue3通过自定义事件更改数据
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>Vue3父向子通过属性进行参数的传递</h3>
<h3>父组件App</h3>
<!--父组件设置监听自定义事件setCount,子组件通过OnsetCount属性传递触发时执行setCountFun函数-->
<!--父组件设置监听事件click,子组件通过Onclick属性传递触发时执行setCountFun1-->
<!--向子组件传递属性count,函数setCountFun-->
<Child @setCount="setCountFun" @click="setCountFun1" :count="count" :setCountFun="setCountFun" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
// :count="count" 前边的count是给子组件传的属性,后边的count是父组件date中的数值
// 注意:在vue3中没有了修饰符.native
// 父组件在子组件上设置的自定义事件,对于子组件而言都会作为子组件的$attrs中的属性来处理。
// 父@click---->子onClick
// 父@setCount---->子onSetCount
// 父组件设置"click"事件,子组件映射为$attrs中"onClick"属性
// 父组件设置"setCount"事件,子组件映射为$attrs中"onSetCount"属性
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import { ref } from "vue";
const count = ref(100);
// 设置一个函数
const setCountFun = function (n: number) {
count.value += n;
console.log("setCountFun is running ")
}
const setCountFun1 = function (n: number) {
count.value += n;
console.log("setCountFun1 is running ")
}
</script>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<!--方式1:子组件监听单击事件,执行子组件获取的属性对应的值的函数-->
<h3 @click="onSetCount(5)">子组件Child</h3>
<h3 @click="onClick(6)">子组件Child1</h3>
<!--方式2:子组件监听单击事件 执行父组件通过props传来的setCountFun-->
<button @click="setCountFun(3)">{{ count }}</button>
<!--方式3:子组件监听单击事件 执行父组件自定义事件函数-->
<!--模版中的$emits可以直接使用,vue3已经自动编译了-->
<button @click="$emits('setCount', 100)">{{ count }}</button>
<button @click="changeCount">{{ count }}</button>
<button @click="changeCount1">{{ count }}</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { onMounted,defineEmits,defineProps } from "vue";
// 获取props传递值
const props = defineProps(["count", "setCountFun", "onClick", "onSetCount"]);
// 在JS中需要通过调用defineEmits 实现vue2中的this.$emit
const $emits = defineEmits(["setCount","click"]);
// 触发自定义事件
const changeCount = () => {
return $emits('setCount',66)
}
const changeCount1 = () => {
return $emits('click', 77)
}
</script>使用案例2
父组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>父组件</h1>
<ChildComponent v-model:myValue="parentValue" />
<p>父组件值: {{ parentValue }}</p>
<!-- 使用 v-model 实现父子双向绑定 -->
<ChildComponent v-model="parentValue" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
components: { ChildComponent },
data() {
return {
parentValue: 'Hello Vue3!', // 父组件的数据
};
},
};
</script>子组件
<template>
<div>
<h2>子组件</h2>
<input v-model="localValue" placeholder="子组件输入框" />
<p>子组件值: {{ localValue }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
myValue: String, // 自定义 prop 名称
},
emits: ['update:myValue'], // 自定义事件名称
computed: {
localValue: {
get() {
return this.myValue;
},
set(value) {
this.$emit('update:myValue', value);
},
},
},
};
</script>状态提升
- 将数据状态放置在共有的父级中。
- 父组件添加自定义事件,子组件通过defineEmits()获取(父元素自定义事件设置的属性名),
- 子组件触发自定义事件调用父组件中的函数来修改父元素数据。
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>App组件</h3>
<button @click="num++">{{num}}</button>
<hr/>
<One @setNum="setNum" :num="num"/>
<hr/>
<Two @setNum="setNum" :num="num"/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import One from "@/components/One";
import Two from "@/components/Two";
import {ref} from "vue";
const num = ref(0);
const setNum = function(v:number=1){
num.value += v;
}
</script>- src->components->One.vue
<template>
<h3>One</h3>
<button @click="changeNum">{{num}}</button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
defineProps(["num"]);
const $emit = defineEmits(["setNum"]);
const changeNum = function(){
$emit("setNum",2)
}
</script>- src->src->components->Two.vue
<template>
<h3>Two</h3>
<button @click="changeNum">{{num}}</button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
defineProps(["num"])
const $emit = defineEmits(["setNum"]);
const changeNum = function(){
$emit("setNum",3)
}
</script>事件总线
Vue.prototype
通过在Vue实例的原型连上增加一个属性 Vue.prototype.$bus 实现事件总线
事件总线的作用
通过使用在Vue原型上设置一个属性(.$bus),把父组件上设置的事件(this.$on("事件名"))和子组件上监听的事件(this.$emit("事件名"))串联起来(父组件和子组件的this不是同一个对象)。
通过使用 Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue()
父组件和子组件在调用 this.$bus 指向的是同一个Vue实例,这就解决了this指向不同对象的问题
事件总线的使用:父组件上设置的事件(this.$bus.$on("事件名"))和子组件上监听的事件(this.$bus.$emit("事件名")),就可以实现父子之间传值。<div id="app">
<button @click="fn">FatherBtn</button>
<hanser ></hanser>
</div><script type="module">
// 在Vue的原型上设置一个全局属性 .$bus
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue();
Vue.component("hanser",{
data(){
return{
num:1
}
},
template:(`
<button @click="Hanser">hanserBtn</button>
`),
methods:{
Hanser(){
// VueComponent的实例;$bus属性在 VueComponent.__proto__.prototype原型上
console.log('子组件中的this',this);
// 子组件设置触发事件 Aqua,并传值
this.$bus.$emit("Aqua","mooooooooo~");
},
},
})
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
age:12
},
methods:{
fn(){
// 父组件设置触发事件 Aqua,并传值
this.$bus.$emit('Aqua',"neeeeeeeee~");
},
},
mounted(){
// Vue的实例;$bus属性在 Vue.prototype上
console.log("父组件中的this",this);
this.$bus.$on('Aqua',function(str){
console.log('Aqua',str)
})
}
})
</script>mitt插件
由于vue3中没有vue2中的Vue.prototype,所以在vue3中无事件总线。可以通过mitt插件实现类似效果
通过调用mitt函数的返回值(自定义为bus)
bus是一个对象
bus有方法emit,on,off,对应:触发,监听,取消事件。
- 下载
npm i mitt- 封装mitt:src->utils->index.ts
import mitt from "mitt";
// 导出一个bus对象
export const bus = mitt();- src->components->One.vue
<template>
<h3>{{num}}</h3>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import {onMounted} from "vue";
import {bus} from "@/utils";
import {defineProps} from 'vue'
defineProps(["num"]);
onMounted(function(){
// 监听一个事件 changenum
bus.on("changenum",()=>{
console.log("ONE->changenum");
// bus.off("changenum");
})
})
</script>- src->components->Two.vue
<template>
<!--方式1-->
<h3 @click="changeNum">{{num}}</h3>
<!--方式2-->
<h3 @click="bus.emit('changenum',300)">{{num}}</h3>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import {bus} from "@/utils";
import {defineProps} from 'vue'
defineProps(["num"]);
// 定义一个函数,触发监听事件
const changeNum = function(){
bus.emit("changenum",200);
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>App组件(父组件){{num}}</h3>
<One :num="num"/>
<Two :num="num"/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {onMounted, ref} from "vue";
import {bus} from "@/utils";
import One from "@/components/One.vue"
import Two from "@/components/Two.vue"
// 定义一个ref对象
const num = ref(100);
onMounted(function(){
// 设置监听事件 changenum
bus.on("changenum",(v)=>{
console.log("APP->changenum",v);
num.value = v as number;
})
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>v-model指令(Vue3)
在Vue3中,v-model不仅可以实现在Vue2中的在单一页面中表单的数据双向绑定,还可以实现父组件和子组件的"Props"属性的双向绑定,实现父子组件数据同步。
v-model设置在子组件上,相当于向子组件传递modelValue和onUpdate:modelValue属性,并且设置了一个自定义update:model-value事件。
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>v-model数据的双向绑定</h3>
<input v-model="userName" type="text"><span>{{ userName }}</span>
<!-- vue3中实现父子组件数据同步 -->
<!-- 通过传递value属性,同时设置自定义事件input -->
<Child :value="userName" @input="setUserName" />
<!-- v-model 实现父子组件数据同步 -->
<!--这些在F12的vue工具中可以看到-->
<!-- 1- 向子组件传递了两个属性:modelValue onUpdate:modelValue -->
<!-- 2- 向子组件传递了自定义事件:update:model-value -->
<Child2 v-model="userName" />
<!-- 相当于写了如下的代码 这里的setUserName是伪代码 -->
<Child2 :modelValue="userName" :onUpdate:modelValue="setUserName" @update:model-value="setUserName" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue"
import Child2 from "@/components/Child2.vue"
let userName = ref("HanserYousa")
// 修改userName的值
const setUserName = function (newName: string) {
console.log("setUserName function is running", newName)
userName.value = newName
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<h3 @click="$my('input','lisi')">我是一个子组件-Child:{{value}}</h3>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
defineProps(["value"]);
const $my = defineEmits(["input"]);
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child2.vue
<template>
<h4>Child2</h4>
<h4>{{ modelValue }}</h4>
<!-- 通过调用传递过来的属性的对应函数改变数值 -->
<button @click="test">onUpdate:modelValue</button>
<!-- 通过触发自定义事件改变数值 -->
<button @click="test2">update:model-value</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
const props = defineProps(["modelValue", "onUpdate:modelValue"]);
const emit = defineEmits(["update:model-value"]);
const test = function () {
// 调用onUpdate:modelValue函数
props["onUpdate:modelValue"]("lisi");
}
const test2 = function () {
emit("update:model-value", "wangwu")
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>多个V-model(Vue3)
v-model使用多个v-model设置在子组件上,相当于向子组件传递多个属性和多个自定义事件。
在子组件接收对应的属性,并且调用自定义事件即可修改父组件的数据状态。
App.vue
<template>
<h3>我是父组件App{{ userName }}</h3>
<Child v-model:userName="userName" v-model:age="age" />
<!-- 上边v-model相当于下边的简写 -->
<!-- handle1,handle2相当于伪代码,vue内部自动实现了 -->
<Child :userName="userName" @update:user-name="handle1" :onUpdate:userName="handle1" :age="age"
:onUpdate:age="handle2" @update:age="handle2" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import { ref } from "vue";
let userName = ref("Hanser");
let age = ref(100)
const handle1 = function (newName: string){
userName.value = newName
}
const handle2 = function (newAge: number) {
age.value = newAge
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>Child.vue
<template>
<h3>我是子组件Child</h3>
<p @click="$emit('update:user-name', userName + '!')">userName:{{ userName }}</p>
<p @click="$emit('update:age', age + 1)">age:{{ age }}</p>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
defineProps(["userName", "age"]);
const $emit = defineEmits(["update:user-name", "update:age"]);
</script>
<style scoped></style>ref指令(Vue3)
Vue3中通过ref指令和ref属性获取子组件的实例。
<template>
<Child ref="child" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
import Child from './Child.vue'
// 创建一个ref空对象
const child = ref(null)
onMounted(() => {
// child.value 是 <Child /> 组件的实例
})
</script>如果一个子组件使用的是选项式 API 或没有使用 <script setup>,被引用的组件实例和该子组件的 this 完全一致,这意味着父组件对子组件的每一个属性和方法都有完全的访问权。这使得在父组件和子组件之间创建紧密耦合的实现细节变得很容易,当然也因此,应该只在绝对需要时才使用组件引用。大多数情况下,你应该首先使用标准的 props 和 emit 接口来实现父子组件交互。
有一个例外的情况,使用了 <script setup> 的组件是默认私有的:一个父组件无法访问到一个使用了 <script setup> 的子组件中的任何东西,除非子组件在其中通过 defineExpose 宏显式暴露:
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const a = 1
const b = ref(2)
// 像 defineExpose 这样的编译器宏不需要导入
defineExpose({
a,
b
})
</script>当父组件通过模板引用获取到了该组件的实例时,得到的实例类型为 { a: number, b: number } (ref 都会自动解包,和一般的实例一样)。
使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>App</h3>
<p>银行账户{{ account }}</p>
<button @click="expenses">支出</button>
<hr />
<Child ref="wallet" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
// 在vue3中没有$children 但是在模块中有$parent
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import { ref } from "vue"
// 定义银行账户
const account = ref(10000000)
// 创建子组件实例
const wallet = ref()
// 支出方法
const expenses = function () {
account.value -= 1000
// wallet.value是子组件实例
wallet.value.money += 1000
}
// 暴漏数据
defineExpose({ account })
</script>
<style scoped></style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<h3>Child</h3>
<p>钱包余额{{ money }}</p>
<button @click="income($parent)">转入</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
// 在vue3中没有$children 但是在模块中有$parent
const money = ref(2000);
// 定义收入方法
const income = function (parent: any) {
money.value -= 100;
parent.account += 100;
}
// 暴漏数据
defineExpose({ money })
</script>
<style scoped></style>$parent(Vue2,Vue3)
$parent 返回当前组件可能存在的父组件实例,如果当前组件是顶层组件,则为 null使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>我是父组件App</h3>
<p>我是父亲,我现在的资产有:{{money}}</p>
<button @click="borrowByChild">向儿子借10元</button>
<hr/>
<Child ref="son"/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
// 在vue3中没有$children,但是在模块中有$parent.
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import {ref} from "vue";
const money = ref(200);
const son = ref();
const borrowByChild = function(){
// 让儿子的资产减少10元
son.value.money -= 10;
// 老子的资产资产加10元
money.value+=10;
}
// 暴漏数据
defineExpose({money})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<h3>我是子组件Child</h3>
<p>我还小,还是个孩子,现在的资产共{{money}}</p>
<button @click="sendFather($parent)">给父亲100元</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {ref} from "vue";
const money = ref(2000);
const sendFather = function(parent:any){
// 儿子减少100
money.value-=100;
// 父亲增加100
parent.money+=100;
}
// 暴漏数据
defineExpose({money})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>provide()和inject()
provide()提供一个值,可以被后代组件注入。
provide()的第一个参数是标识,第二个参数是数据状态。
提供数据,让自己所包裹的组件(可以隔代)使用。
可以被自己直接包裹或间接包裹的组件获取到数据。
通过provide传递,通过inject接收。接收之后数据可以修改,并支持响应式。
provide() 提供值
详细信息
provide() 接受两个参数:第一个参数是要注入的 key,可以是一个字符串或者一个 symbol,第二个参数是要注入的值。
当使用 TypeScript 时,key 可以是一个被类型断言为 InjectionKey 的 symbol。InjectionKey 是一个 Vue 提供的工具类型,继承自 Symbol,可以用来同步 provide() 和 inject() 之间值的类型。
与注册生命周期钩子的 API 类似,provide() 必须在组件的 setup() 阶段同步调用。示例
<script setup>
import { ref, provide } from 'vue'
import { countSymbol } from './injectionSymbols'
// 提供静态值
provide('path', '/project/')
// 提供响应式的值
const count = ref(0)
provide('count', count)
// 提供时将 Symbol 作为 key
provide(countSymbol, count)
</script>inject() 注入值到组件
通过inject()方法,可以获取到被自己直接包裹或间接包裹的组件的数据。(兄弟之间无法使用)
通过provide传递,通过inject接收。接收之后数据可以修改,并支持响应式。
注入一个由祖先组件或整个应用 (通过
app.provide()) 提供的值、inject()的参数是provide()中的标识。
详细信息
第一个参数是注入的 key。Vue 会遍历父组件链,通过匹配 key 来确定所提供的值。如果父组件链上多个组件对同一个 key 提供了值,那么离得更近的组件将会“覆盖”链上更远的组件所提供的值。如果没有能通过 key 匹配到值,`inject()` 将返回 `undefined`,除非提供了一个默认值。
第二个参数是可选的,即在没有匹配到 key 时使用的默认值。
第二个参数也可以是一个工厂函数,用来返回某些创建起来比较复杂的值。在这种情况下,你必须将 `true` 作为第三个参数传入,表明这个函数将作为工厂函数使用,而非值本身。
与注册生命周期钩子的 API 类似,`inject()` 必须在组件的 `setup()` 阶段同步调用。
当使用 TypeScript 时,key 可以是一个类型为 `InjectionKey` 的 symbol。`InjectionKey` 是一个 Vue 提供的工具类型,继承自 `Symbol`,可以用来同步 `provide()` 和 `inject()` 之间值的类型。示例
假设有一个父组件已经提供了一些值,如前面 provide() 的例子中所示:
<script setup>
import { inject } from 'vue'
import { countSymbol } from './injectionSymbols'
// 注入不含默认值的静态值
const path = inject('path')
// 注入响应式的值
const count = inject('count')
// 通过 Symbol 类型的 key 注入
const count2 = inject(countSymbol)
// 注入一个值,若为空则使用提供的默认值
const bar = inject('path', '/default-path')
// 注入一个值,若为空则使用提供的函数类型的默认值
const fn = inject('function', () => {})
// 注入一个值,若为空则使用提供的工厂函数
const baz = inject('factory', () => new ExpensiveObject(), true)
</script>使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>我是父组件App(爷爷):{{token}}</h3>
<p>age:{{age}}</p>
<hr/>
<Child/>
<hr/>
<Child2/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import Child2 from "@/components/Child2.vue";
import {ref, provide, inject} from "vue";
const token = ref("appToken");
// 第一个参数是标识,第二个参数是数据状态
provide("t",token);// 提供数据,让自己所包裹的组件(可以隔代)使用。
const age = inject("age");
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->component->Child.vue
<template>
<h3 @click="t+='!'">我是子组件Child(儿子):{{t}}</h3>
<hr/>
<One/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import One from "@/components/One.vue"
import {inject, provide, ref} from "vue";
// 定义一个ref实例
const age = ref(100);
// 注入值到自己
const t = inject("t");
// 提供值
provide("age",age);
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>- src->component->grandson.vue
<template>
<h3 @click="t+='?'">One组件--孙子:{{t}}</h3>
<p>来自于child的age:{{age}}</p>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {inject} from "vue";
// 注入爷爷辈 t属性
const t = inject("t");
// 注入父亲辈 age属性
const age = inject("age");
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>作用域插槽(Vue2,Vue3)
插槽类似于路由,有入口和出口
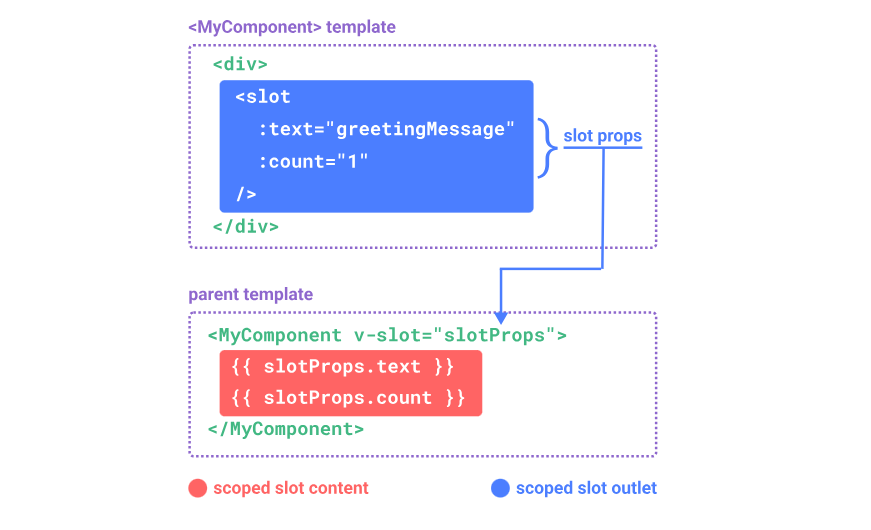
src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>App</h3>
<Child>
<!--把template包裹的标签放置在子组件对应的slot标签中渲染 -->
<!-- 入口 -->
<!--slotProps用于接收子组件传来的属性-->
<template v-slot="slotProps">
<p>{{ slotProps.userName }}</p>
<p>{{ slotProps.age }}</p>
</template>
</Child>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
import { ref } from "vue";
</script>src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<h3>Child</h3>
<!--父组件template标签内的数据默认在slot标签位置渲染-->
<!-- 出口 -->
<!-- 向父组件传递 userName和age属性 -->
<slot :userName="userName" :age="age"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 定义一个ref实例
const userName = ref("hanser")
const age = ref(18)
// 暴漏数据
defineExpose({ userName, age })
</script>作用域插槽作用:可以实现子组件向父组件传递属性
使用案例
- src->App.vue
<template>
<h3>App</h3>
<Child>
<!--把template包裹的标签放置在子组件对应的slot标签中渲染 -->
<!-- 入口 -->
<!--slotProps用于接收子组件传来的属性-->
<template v-slot="slotProps">
<p>{{ slotProps.userName }}</p>
<p>{{ slotProps.age }}</p>
</template>
</Child>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import Child from "@/components/Child.vue";
</script>- src->components->Child.vue
<template>
<h3>Child</h3>
<!-- 向父组件传递 userName和age属性 -->
<!--父组件template标签内的数据默认在slot标签位置渲染-->
<!-- 出口 -->
<slot :userName="userName" :age="age"></slot>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 获取父组件的属性 info
const props = defineProps(["food"]);
// 定义一个ref实例
const userName = ref("hanser")
const age = ref(18)
// 暴漏数据
defineExpose({ userName, age })
</script>